Menu
Prompt Praxis Laboratories provides a full range of rapid testing and support services focusing on pharmaceutical products and compounded sterile or nonsterile preparations.
Prompt Praxis Labs helps you in designing, developing, implementing and managing an effective, safe and secure Analytical Testing Program for a Pharma Product. We offer the test methods listed below for analyzing a product’s strength, quality, purity, potency, and identity. We also provide services for analytical characterization, bioanalytical services, method development and validation, as well as method transfer and assistance.
Click on each test method to see a sample chromatogram.
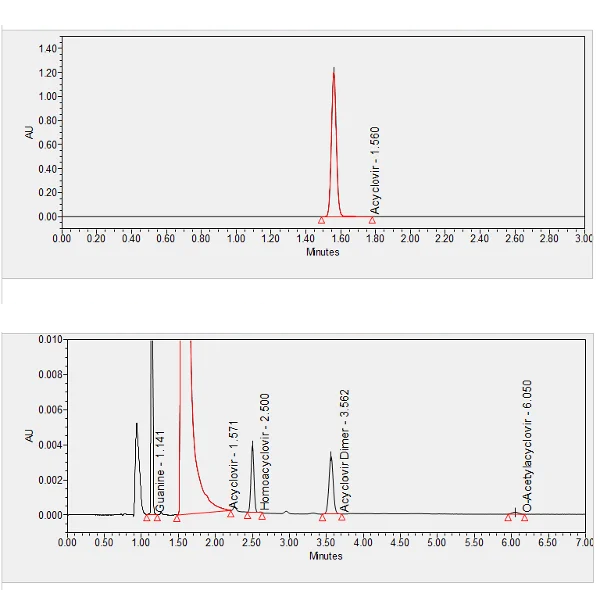
Acyclovir is a medication used to manage and treat infections caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is FDA approved to treat genital herpes and HSV encephalitis. Some off-label uses include cold sores, shingles, and chickenpox. It is in the antiviral class of medications. **
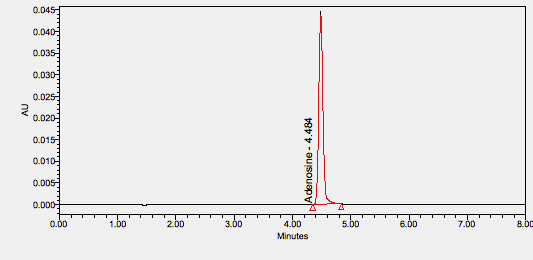
Adenosine has uses as both a diagnostic or therapeutic agent. As a diagnostic agent, adenosine can be utilized in myocardial perfusion stress imaging due to its vasodilatory effects. As a therapeutic agent, adenosine can be used due to its antiarrhythmic properties in supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). **
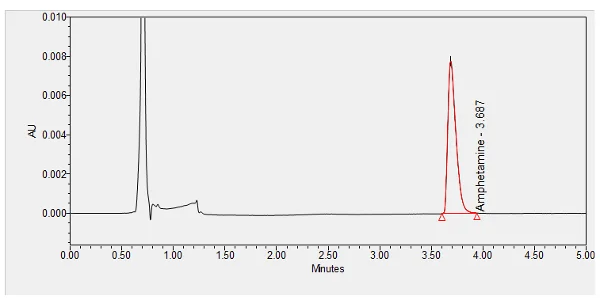
Dextroamphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and an amphetamine enantiomer[note 1] that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy.[1][17] It is also used as an athletic performance and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. ***
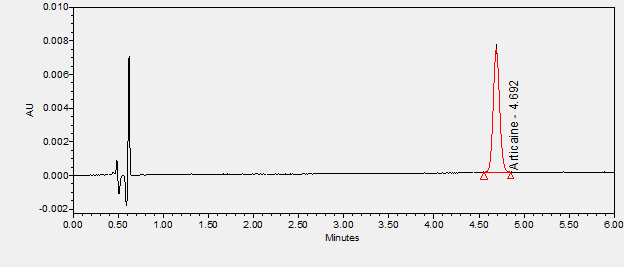
Articaine is an intermediate-potency, short-acting amide local anesthetic with a fast metabolism due to an ester group in its structure. It is effective with local infiltration or peripheral nerve block in dentistry, when administered as a spinal, epidural, ocular, or regional nerve block, or when injected intravenously for regional anesthesia. In comparative trials, its clinical effects were not generally significantly different from those of other short-acting local anesthetics like lidocaine, prilocaine, and chloroprocaine, and there is no conclusive evidence demonstrating above-average neurotoxicity. Articaine proved to be suitable and safe for procedures requiring a short duration of action in which a fast onset of anesthesia is desired, eg, dental procedures and ambulatory spinal anesthesia, in normal and in special populations.**
Amiodarone is one of the most commonly used anti-arrhythmic drugs. While the United States FDA has labeled amiodarone for the treatment of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, the drug is commonly used off-label to treat supraventricular tachyarrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation as well as for the prevention of ventricular tachyarrhythmias (VTs) in high-risk patients. **
Atropine or atropine sulfate carries FDA indications for anti-sialagogue/anti-vagal effect, organophosphate/muscarinic poisoning, and bradycardia. Atropine acts as a competitive, reversible antagonist of muscarinic receptors: an anticholinergic drug. **
Baclofen is used to treat muscle spasticity; it is FDA-approved for managing reversible spasticity, particularly for the relief of flexor spasms, clonus, and concomitant pain, common sequelae of spinal cord lesions, and multiple sclerosis. Baclofen also has several off-label uses. **
Benzalkonium chlorides (BACs) are chemicals with widespread applications due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This review provides an overview of the market for BACs, as well as regulatory measures and available data on safety, toxicity, and environmental contamination. We focus on the effect of frequent exposure of microbial communities to BACs and the potential for cross-resistant phenotypes to emerge. Toward this goal, we review BAC concentrations in consumer products, their correlation with the emergence of tolerance in microbial populations, and the associated risk potential. Our analysis suggests that the ubiquitous and frequent use of BACs in commercial products can generate selective environments that favor microbial phenotypes potentially cross-resistant to a variety of compounds. An analysis of benefits versus risks should be the guidepost for regulatory actions regarding compounds such as BACs.**
Benzethonium chloride is a (synthetic) quaternary ammonium salt that is benzyldimethylamine in which the nitrogen is quaternised by a 2-{2-[p-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy]ethoxy}ethyl group, with chloride as the counter-ion. An antiseptic and disinfectant, it is active against a broad spectrum of bacteria, fungi, moulds and viruses. It has a role as an antiseptic drug, a disinfectant, an antibacterial agent, an antiviral agent and an antifungal agent. It is a quaternary ammonium salt, a chloride salt and an aromatic ether. **
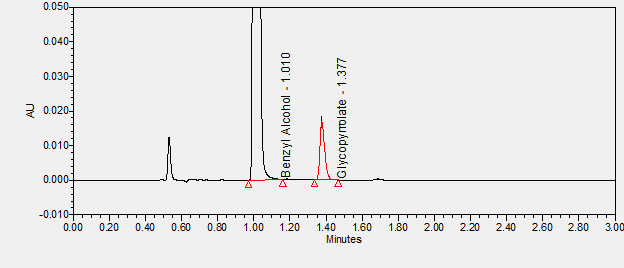
Benzyl alcohol appears as a clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. Slightly denser than water. Flash point 194°F. Boiling point 401°F. Contact may irritate skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. May be slightly toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals.**
Bevacizumab is used to treat a certain type of brain tumor, and certain types of cancers of the kidney, liver, lung, colon, rectum, cervix, ovary, or fallopian tube. Bevacizumab is also used to treat cancer of the membrane lining the internal organs in your abdomen. It is usually given as part of a combination of cancer medicines.*
Bromfenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) for ophthalmic use. Ophthalmic NSAIDs are becoming a cornerstone for the management of ocular pain and inflammation. Their well-characterized anti-inflammatory activity, analgesic property, and established safety record have also made NSAIDs an important tool for optimizing surgical outcomes. Non-ophthalmic formulations of bromfenac were withdrawn in the US in 1998 due to cases of severe liver toxicity.****
Bupivacaine is a potent local anesthetic with unique characteristics from the amide group of local anesthetics. Local anesthetics are used in regional anesthesia, epidural anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, and local infiltration. Local anesthetics generally block the generation of the action potential in nerve cells by increasing the threshold for electrical excitation.**
Butorphanol is an opioid agonist-antagonist used to treat moderate to severe pain.****
Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a salt with the chemical formula CaCl2. It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and it is highly soluble in water. It can be created by neutralising hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide.*

Calcium gluconate is a medication used to manage hypocalcemia, cardiac arrest, and cardiotoxicity due to hyperkalemia or hypermagnesemia. It is classified as a calcium salt. This activity outlines the indications, action, and contraindications for calcium gluconate as a valuable agent in managing hypocalcemia, cardiac arrest, cardiotoxicity due to hyperkalemia or hypermagnesemia, and other disorders as applicable. This activity will highlight the mechanism of action, adverse events, and other key factors (e.g., off-label uses, dosing, pharmacodynamics, monitoring, relevant interactions). **

Cantharidin is a naturally occurring odorless, colorless fatty substance of the terpenoid class that is produced as an oral fluid in the alimentary canal of the male blister beetle 1,2. For its natural purpose, the male blister beetle secretes and presents the cantharidin to a female beetle as a copulatory gift during mating. Post-copulation, the female beetle places the cantharidin over her eggs as protection against any potential predators.
Available synthetically since the 1950s, topical applications of cantharidin have been used predominantly as a treatment for cutaneous warts since that time 1,2. In 1962 however, marketers of cantharidin failed to produce sufficient efficacy data, resulting in the FDA revision of approval of cantharidin.****
Cefazolin is a beta-lactam antibiotic and first-generation cephalosporin with bactericidal activity. Cefazolin binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Inactivation of PBPs interferes with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. This results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis.***
Ceftazidime is an injected broad-spectrum third-generation cephalosporin beta-lactam antibiotic used to treat or prevent a variety of bacterial infections, including pneumonia, gynecological infections, bone and joint infections, and septicemia, among others.****
Ceftriaxone is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of bacterial infections in various locations, such as in the respiratory tract, skin, soft tissue, and urinary tract.****
Cefuroxime is a cephalosporin indicated for the treatment of a variety of infections including acute bacterial otitis media, several upper respiratory tract infections, skin infections, urinary tract infections, gonorrhea, early Lyme disease, and impetigo.****
Cisatracurium besylate is an intermediate-acting, non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking drug (NMBD). Cisatracurium has a benzylisoquinolinium structure and is the 1R cis-1-prime R cis isomer of atracurium. As an NMBD, it has found use as an adjunct to general anesthesia facilitating tracheal intubation and providing skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery. It may also be used to provide skeletal muscle relaxation to facilitate mechanical ventilation in an intensive care unit setting, but must be used with sedation. **
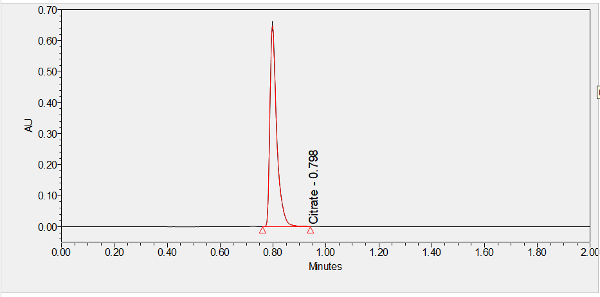
Citrate is a buffering excipient often used in injectable formations.
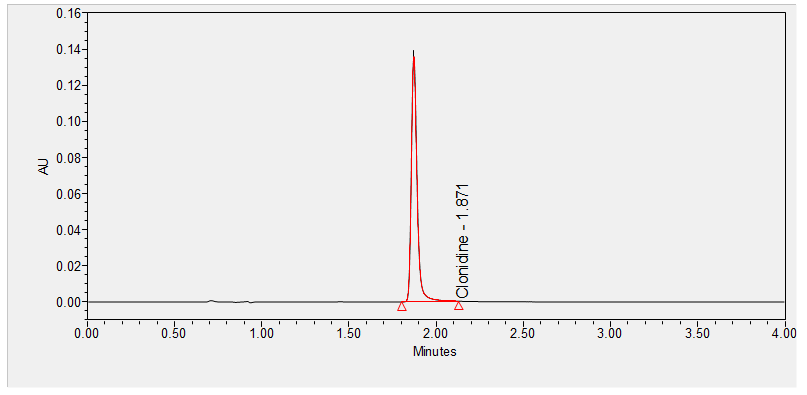
Clonidine is an antihypertensive medication that acts on alpha-adrenergic and imidazoline receptor agonists. Clonidine is an antihypertensive drug that lowers blood pressure and heart rate by relaxing the arteries and increasing the blood supply to the heart; it has other FDA-approved indications such as treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children (FDA approval 2010); management of tics commonly found with Tourette syndrome; and adjunct therapy for severing cancer-related pain.**
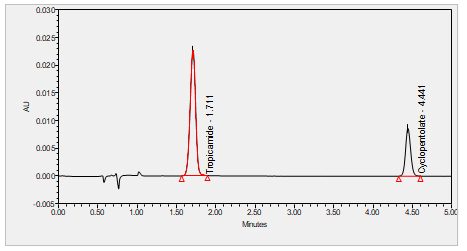
Cyclopentolate is a muscarinic antagonist. It is commonly used as an eye drop during pediatric eye examinations to dilate the eye (mydriatic) and prevent the eye from focusing/accommodating (cycloplegic). Cyclopentolate or atropine can also be administered to reverse muscarinic and central nervous system effects of indirect cholinomimetic (anti-AChase) administration.***
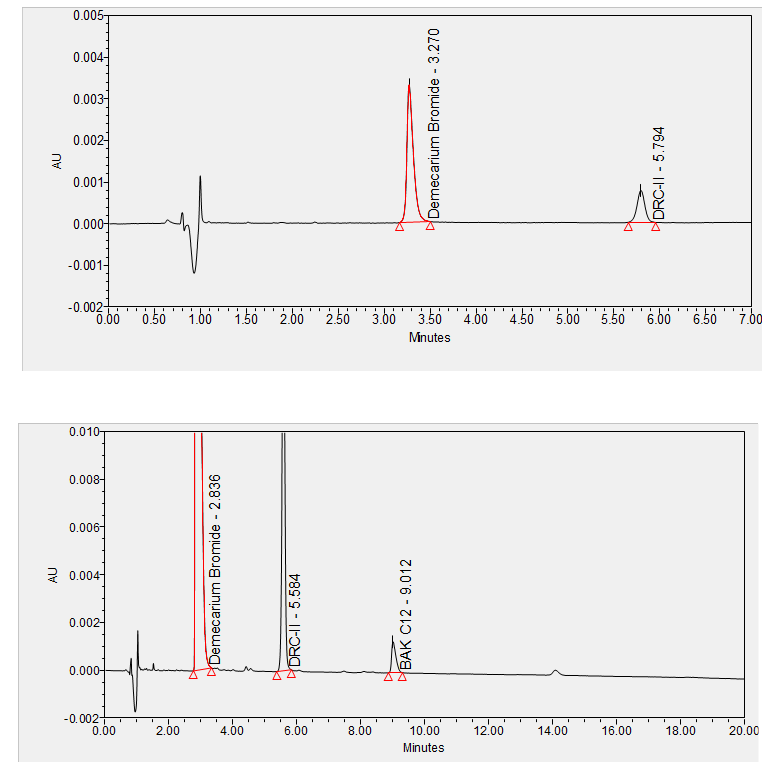
Demecarium is an indirect-acting parasympathomimetic agent that is used to treat glaucoma. It is a cholinesterase inhibitor or an anticholinesterase. Cholinesterase inhibitors prolong the effect of acetylcholine, which is released at the neuroeffector junction of parasympathetic postganglion nerves, by inactivating the cholinesterases that break it down. Demecarium inactivates both pseudocholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase. In the eye, this causes constriction of the iris sphincter muscle (causing miosis) and the ciliary muscle. The outflow of the aqueous humor is facilitated, which leads to a reduction in intraocular pressure. ****
Desmopressin is a drug that acts on the vasopressin receptors of the body. It has many relevant clinical uses, ranging from nocturnal enuresis to hemophilia. While this drug is relatively safe to use, there are certain side effects to be kept in mind for patients receiving the drug, as well as specific contraindications that limit the population that can receive desmopressin. **
Dexmedetomidine, sold under the trade name Precedex among others, is a medication used for sedation. It is also used to treat acute agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder.
Similar to clonidine, it is a sympatholytic drug that acts as an agonist of α2-adrenergic receptors in certain parts of the brain. Veterinarians use dexmedetomidine for similar purposes in treating cats, dogs, and horses. It was developed by Orion Pharma.***
Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate is a sodium phosphate salt form of Dexamethasone, a synthetic adrenal corticosteroid with potent anti-inflammatory properties. In addition to binding to specific nuclear steroid receptors, dexamethasone also interferes with NF-kB activation and apoptotic pathways. This agent lacks the salt-retaining properties of other related adrenal hormones. (NCI04)**
Diltiazem is a benzothiazepine derivative with antihypertensive and vasodilating properties. Approved in 1982 by the FDA, it is a member of the non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers drug class. It works through various mechanisms of action, but it primarily works by inhibiting the calcium influx into cardiac and vascular smooth muscle during depolarization.12 Compared to dihydropyridine drugs, such as nifedipine, that preferentially act on vascular smooth muscle and verapamil that directly acts on the heart muscle, diltiazem displays an intermediate specificity to target both the cardiac and vascular smooth muscle.8 Being a potent vasodilator, diltiazem is used clinically as an antihypertensive, anti-arrhythmic, and as an anti-anginal agent 9 for the management of cardiovascular conditions such as hypertension, chronic stable angina, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter. Apart from its main FDA-approved indications, diltiazem has also been used for numerous off-label indications, such as anal fissures (in topical formulations), migraine prophylaxis, pulmonary hypertension, and rest-related cramps in the lower extremities.9 Typically available in extended-release oral and intravenous formulations, diltiazem is marketed under various brand names with Cardizem and Tiazac being the most common ones. ***
The FDA approveD dobutamine for short-term use in patients with decreased contractility due to heart failure or cardiac surgical procedures leading to cardiac decompensation. The agent has not been shown to give positive outcomes in the hospitalized or outpatient setting for heart failure patients despite hemodynamically improving the patient's condition. Dobutamine can be used as temporary intravenous inotropic support until resolution of the acute inducing factors or the patient receives more definitive treatment, such as coronary revascularization, mechanical circulatory support, or heart transplant. Short-term intravenous inotropic support should be given to patients in cardiogenic shock to preserve systemic blood flow and protect from end-organ damage. **
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals.***
Edetate disodium (EDTA) is a chelating agent. A chelating agent is capable of removing a heavy metal, such as lead or mercury, from the blood. EDTA is also used to lower blood levels of calcium when they have become dangerously high.
EDTA can also used to control heart rhythm disturbances caused by a heart medication called digitalis (digoxin, Lanoxin).

Ephedrine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is often used to prevent low blood pressure during anesthesia. It has also been used for asthma, narcolepsy, and obesity but is not the preferred treatment. It is of unclear benefit in nasal congestion. It can be taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle, vein, or just under the skin. Onset with intravenous use is fast, while injection into a muscle can take 20 minutes, and by mouth can take an hour for effect. When given by injection it lasts about an hour and when taken by mouth it can last up to four hours. ***
Epinephrine is a hormone and neurotransmitter used to treat allergic reactions, to restore cardiac rhythm, and to control mucosal congestion, glaucoma, and asthma.****
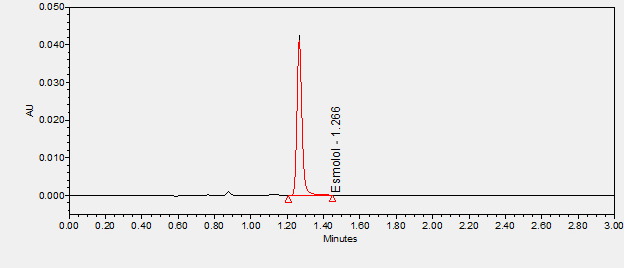
Esmolol is a cardioselective beta-adrenergic blocker used for the short-term control of ventricular rate and heart rate in various types of tachycardia, including perioperative tachycardia and hypertension.****
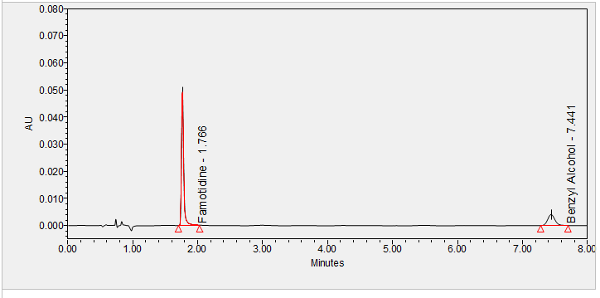
Famotidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist used to treat duodenal ulcers, benign gastric ulcers, GERD, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.****
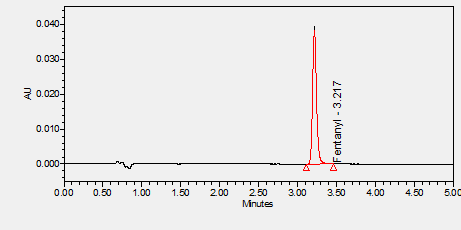
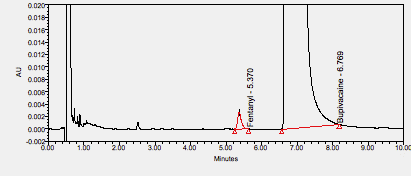
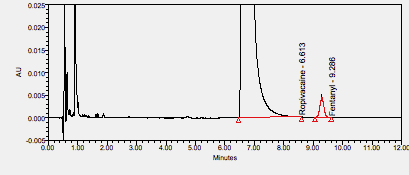
Fentanyl is an opioid analgesic used in anesthesia, for breakthrough cancer pain, or round the clock pain management.****
Bupivacaine is a local anesthetic used in a wide variety of superficial and invasive procedures.****
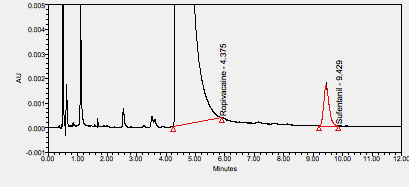
Ropivacaine is an amide-type local anesthetic used for local or regional anesthesia during surgery and for short-term management of acute pain.****
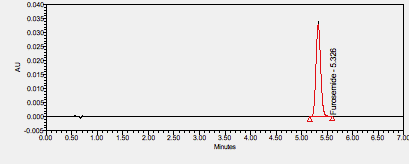
Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat hypertension and edema in congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, renal disease, and hypertension.****
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside used to treat a wide variety of aerobic infections in the body.****
Glycopyrronium is an anticholinergic agent used to treat hyperhidrosis, severe drooling, COPD, used with other medications to treat ulcers, and used in anesthesia.****
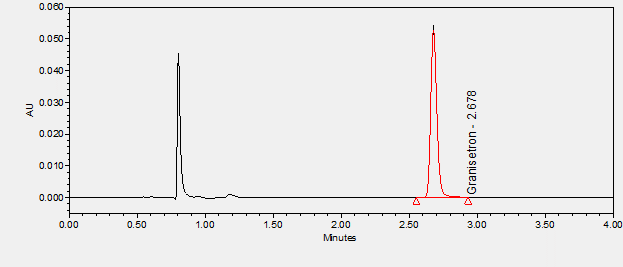
Granisetron is a 5HT3 antagonist used to treat nausea and vomiting in cancer therapy and postoperatively.****
Heparin is an anticoagulant indicated for thromboprophylaxis and to treat thrombosis associated with a variety of conditions such as pulmonary embolism and atrial fibrillation.****
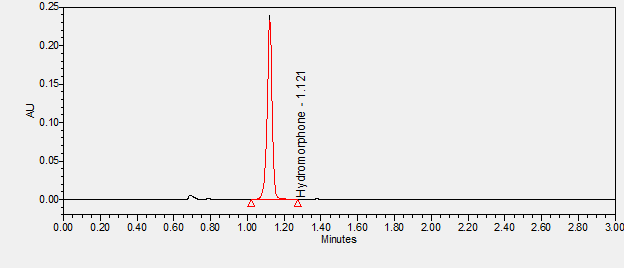
Hydromorphone is a medication used in the management and treatment of moderate to severe acute pain as well as severe chronic pain. It is in the opioid class of medications. **
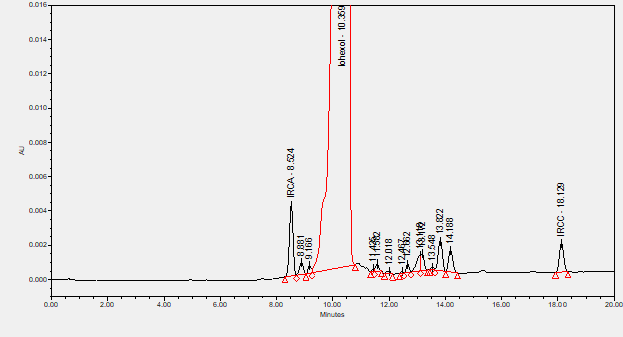
Iohexol is a contrast agent for intrathecal administration used in myelography and contrast enhancement for computerized tomography.****
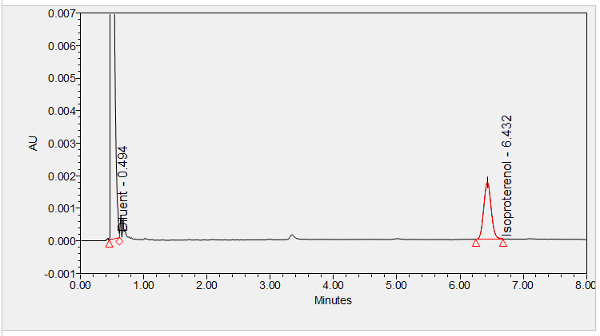
Isoprenaline is a catecholamine non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist typically used to treat bradycardia and heart block. ****
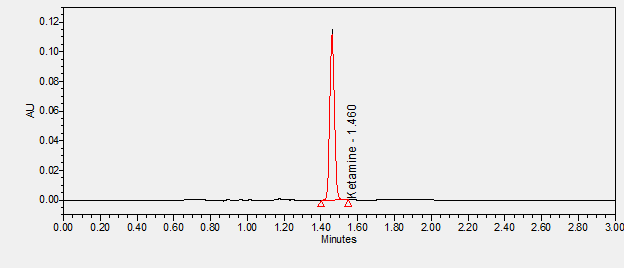
Ketamine is a rapid-acting general anesthetic and NMDA receptor antagonist used for induction of anesthesia diagnostic and surgical procedures typically in combination with a muscle relaxant.****
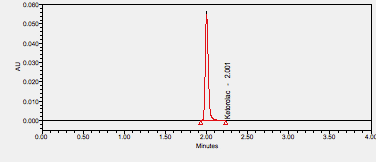
Ketorolac is an NSAID used to treat moderate to severe pain, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, menstrual disorders, and headaches.****
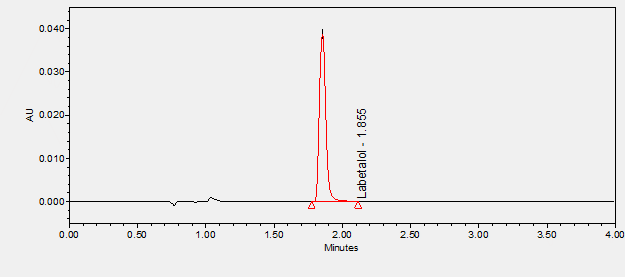
Labetalol is an alpha and beta adrenergic antagonist used to treat hypertension, angina, and sympathetic overactivity syndrome.****
Oxymetazoline is an alpha-1A adrenoceptor agonist used to treat nasal congestion, allergic reactions of the eye, and facial erythema associated with rosacea.****
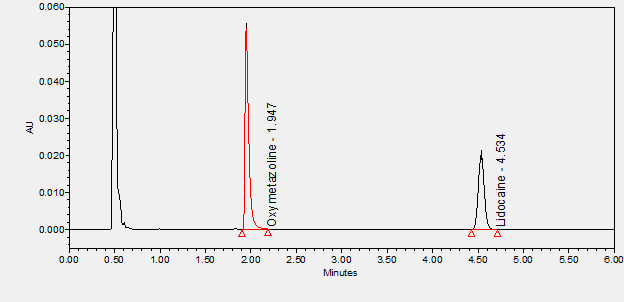
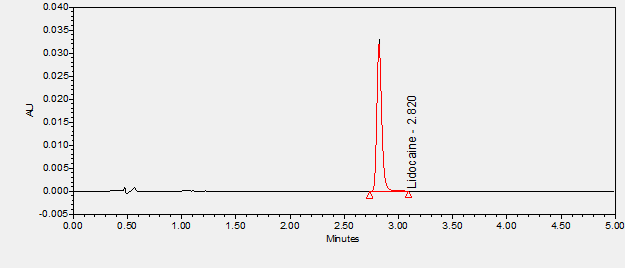
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic used in a wide variety of superficial and invasive procedures.****
Lorazepam is a short-acting benzodiazepine commonly used to treat panic disorders, severe anxiety, and seizures.****
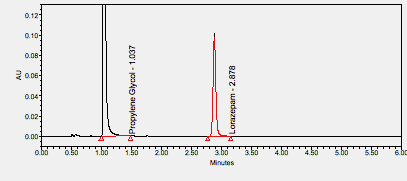
Magnesium citrate is a laxative used in bowel preparation for colonoscopy or as a magnesium supplement. ****
Magnesium sulfate is a drug used to treat convulsions during pregnancy, nephritis in children, magnesium deficiency, and tetany. ****
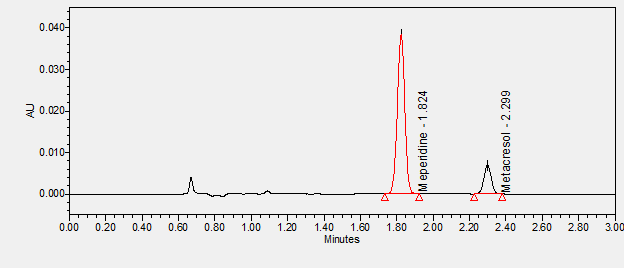
Meperidine is an opioid agonist with analgesic and sedative properties used to manage severe pain.****
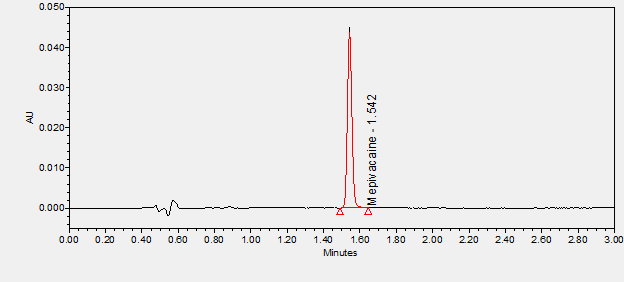
Mepivacaine is a local anesthetic used for local or regional analgesia or anesthesia. A local anesthetic that is chemically related to bupivacaine but pharmacologically related to lidocaine. It is indicated for infiltration, nerve block, and epidural anesthesia. Mepivacaine is effective topically only in large doses and therefore should not be used by this route. (From AMA Drug Evaluations, 1994, p168). ****
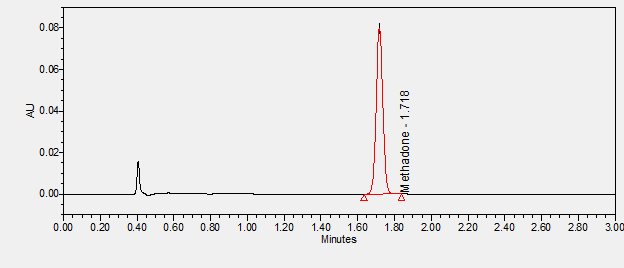
Methadone is an opioid analgesic indicated for management of severe pain that is not responsive to alternative treatments. Also used to aid in detoxification and maintenance treatment of opioid addiction.****
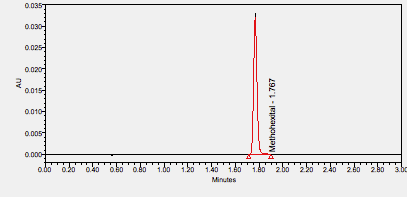
Methohexital is an anesthetic used to induce deep sedation. An intravenous anesthetic with a short duration of action that may be used for induction of anesthesia. ****
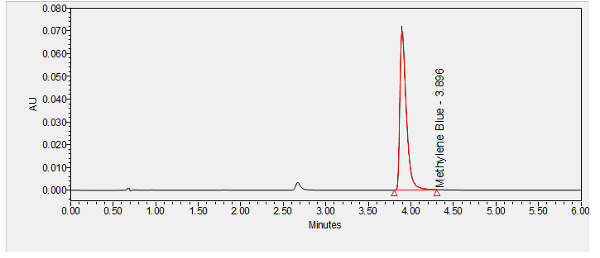
Methylene blue is an oxidation-reduction agent used for the treatment of pediatric and adult patients with acquired methemoglobinemia. ****
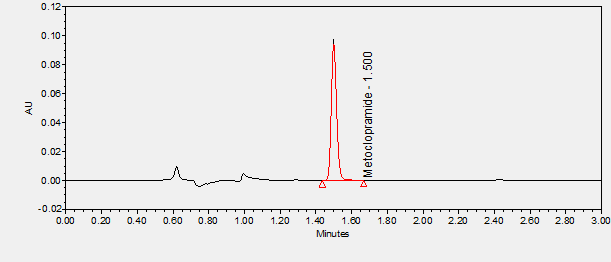
Metoclopramide is an antiemetic agent and dopamine D2 antagonist used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease, prevention of nausea and vomiting, and to stimulate gastric emptying. ****
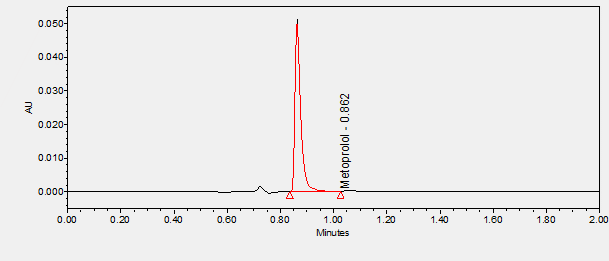
Metoprolol is a beta-blocker used in the treatment of hypertension and angina, and used to reduce mortality due to myocardial infarction. ****
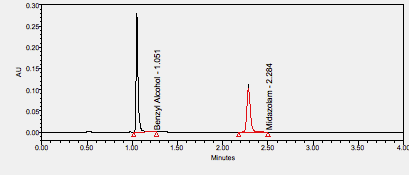
Midazolam is a short-acting injectable benzodiazepine with rapid onset that is commonly used in seizures, anesthesia and anxiety disorders. ****
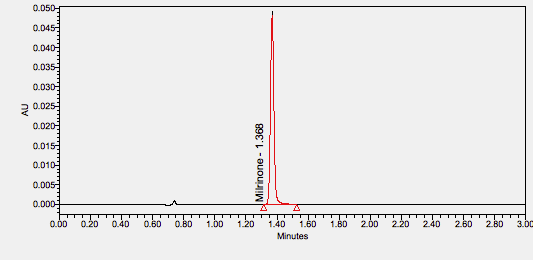
Milrinone is a PDE-III inhibitor with inotropic, lusitropic, and vasodilatory properties used for the short-term treatment of acute decompensated heart failure. ****
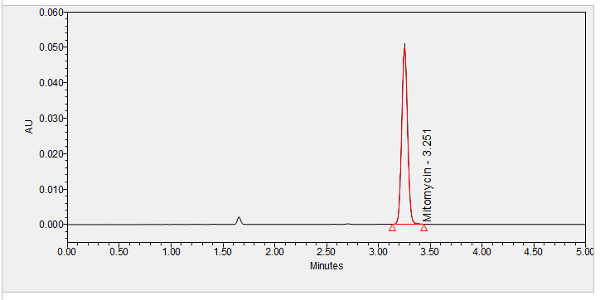
Mitomycin is an antimetabolite used as an adjunct to ab externo (outside approach) eye surgeries for the treatment of glaucoma and used as a chemotherapeutic agent for various malignancies. ****
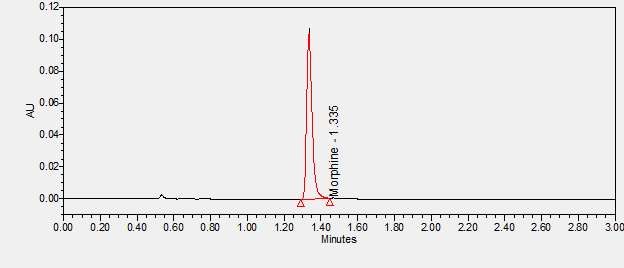
Morphine is an opioid agonist used for the relief of moderate to severe acute and chronic pain. ****
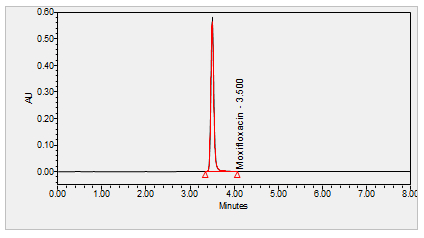
Moxifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. Moxifloxacin is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic agent. Bayer AG developed the drug (initially called BAY 12-8039) and it is marketed worldwide (as the hydrochloride) under the brand name Avelox (in some countries also Avalox) for oral treatment. ****
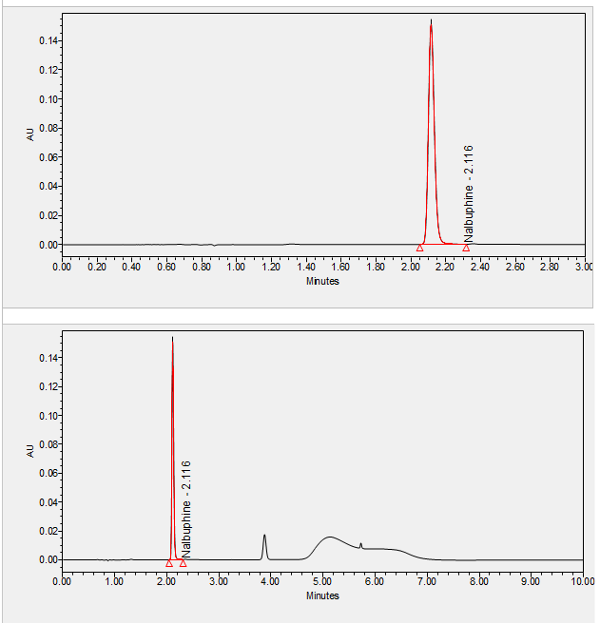
Nalbuphine is an opioid agonist-antagonist used to treat pain, for pre and postoperative analgesia, and for analgesia in labor and delivery. ****
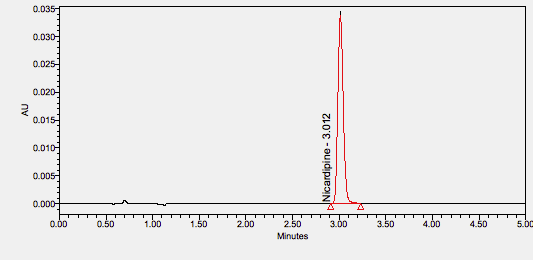
Nicardipine is a calcium channel blocker used for the short-term treatment of hypertension and chronic stable angina. ****
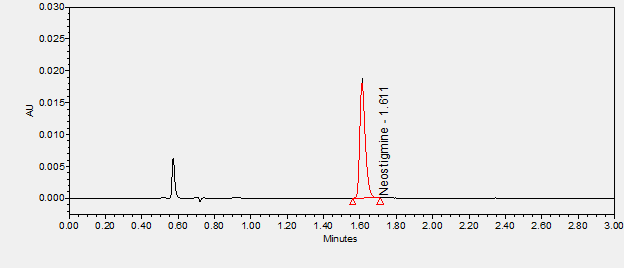
Neostigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor used in the symptomatic treatment of myasthenia gravis by improving muscle tone. ****
Nitroglycerin is a nitrate vasodilator used to treat or prevent angina, heart failure, hypertension, and anal fissures. ****
Norepinephrine is a sympathomimetic used in the control of blood pressure during various hypotensive states and as an adjunct treatment during cardiac arrest. ****
Ondansetron is a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist used to prevent nausea and vomiting in cancer chemotherapy and postoperatively. ****
Oxymetazoline is an alpha-1A adrenoceptor agonist used to treat nasal congestion, allergic reactions of the eye, and facial erythema associated with rosacea. ****
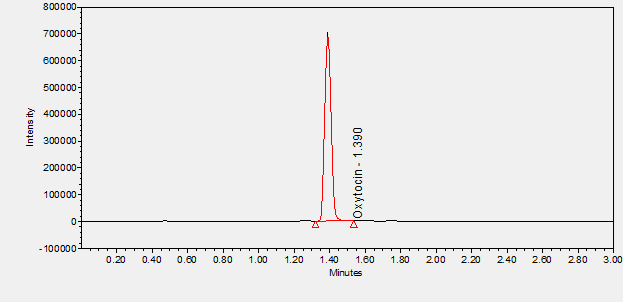
Oxytocin is a recombinant hormone used to induce or strengthen uterine contractions in pregnant women to aid in labor and delivery or to control postpartum bleeding. ****
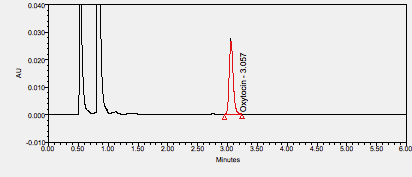
Oxytocin is a recombinant hormone used to induce or strengthen uterine contractions in pregnant women to aid in labor and delivery or to control postpartum bleeding. ****
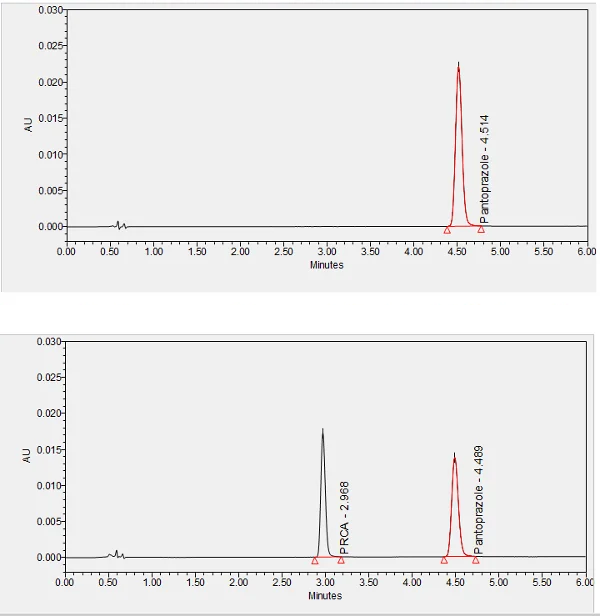
Pantoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor used to treat erosive esophagitis, gastric acid hypersecretion, and to promote healing of tissue damage caused by gastric acid. ****
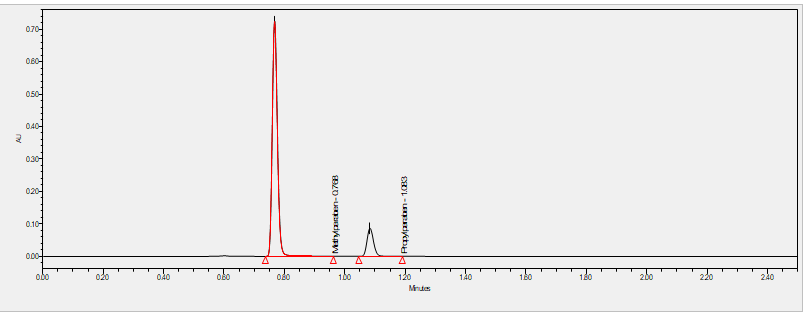
Parabens are a class of widely used preservatives in cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. Chemically, they are a series of parahydroxybenzoates or esters of parahydroxybenzoic acid (also known as 4-hydroxybenzoic acid). Parabens are effective preservatives in many types of formulas. These compounds, and their salts, are used primarily for their bactericidal and fungicidal properties. They are found in shampoos, commercial moisturizers, shaving gels, personal lubricants, topical/parenteral pharmaceuticals, suntan products, makeup, and toothpaste. They are also used as food preservatives. ***
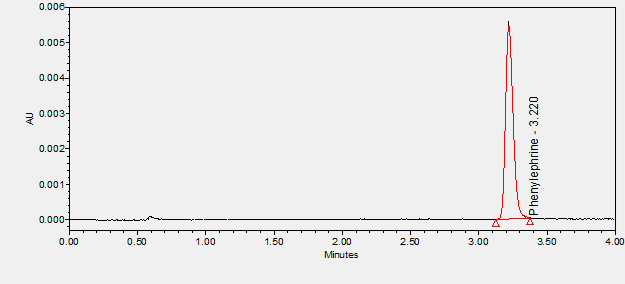
Phenylephrine is an alpha-1 adrenergic agonist used in the management of hypotension, generally in the surgical setting associated with the use of anesthetics. ****
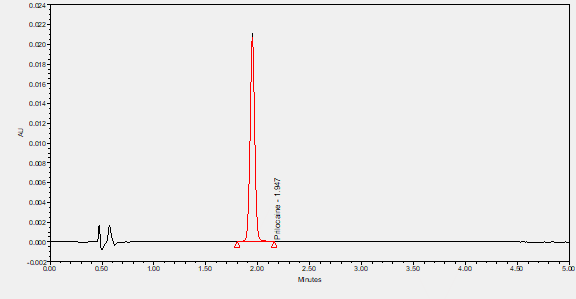
Prilocaine is a local anesthetic used in dental procedures. It is a local anesthetic that is similar pharmacologically to lidocaine. Currently, it is used most often for infiltration anesthesia in dentistry. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1992, p165). ****
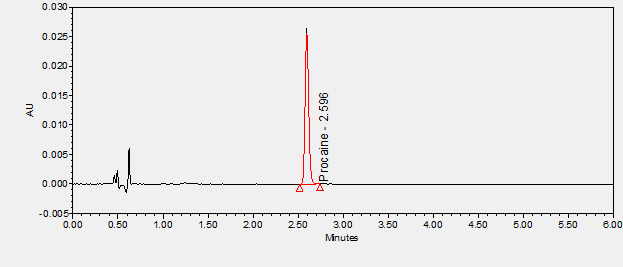
Procaine is a local anesthetic used for anesthesia, peripheral nerve block, and spinal nerve block. ****
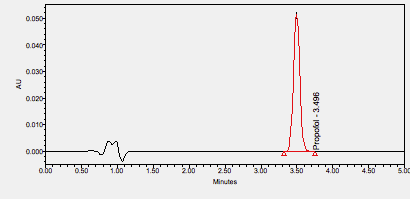
Propofol is a medication used in general anesthesia and for sedation. ****
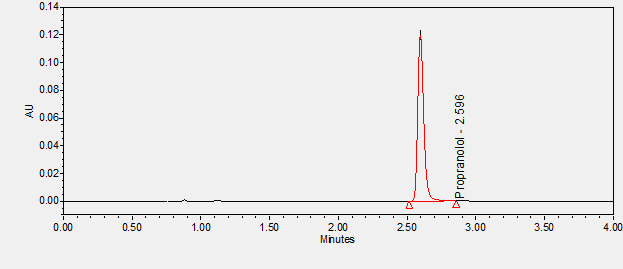
Propranolol is a non-selective beta adrenergic antagonist used to treat hypertension, angina, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, migraine, essential tremor, hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, and pheochromocytoma. ****
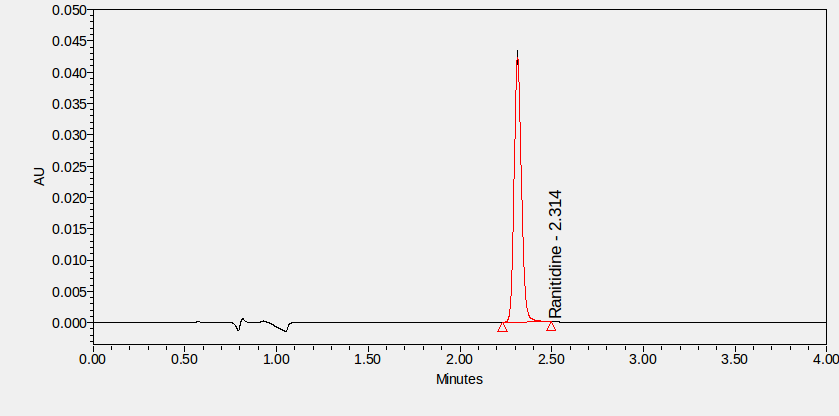
Ranitidine is a commonly used drug, classified as a histamine H2-receptor antagonist, and belongs to the same drug class as cimetidine and famotidine. This drug helps to prevent and treat gastric-acid associated conditions, including ulcers, because of its ability to decrease gastric acid secretion.2,11 Ranitidine is often referred to as Zantac, and is available in various forms, including tablet, injection, and effervescent tablet preparations.11,14
The prevalence of GERD is thought to be 10-20% in western countries.4 Ranitidine has proven to be an effective treatment for relieving uncomfortable symptoms of gastric acid associated conditions and is therefore widely used in GERD and other gastric-acid related conditions.5,11 ****
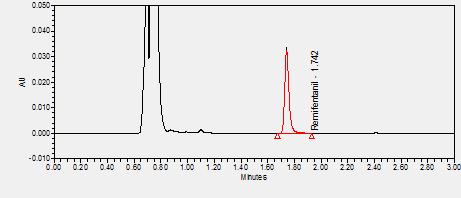
Remifentanil (marketed by Abbott as Ultiva) is a potent ultra short-acting synthetic opioid given to patients during surgery for pain relief and adjunctive to an anaesthetic. Remifentanil is a specific mu-type-opioid receptor agonist which means it reduces sympathetic nervous system tone, and causes respiratory depression and analgesia. ****
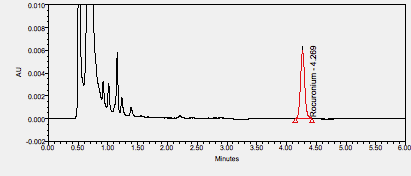
Rocuronium (rapid onset-curonium) is a desacetoxy analogue of vecuronium with a more rapid onset of action. It is an aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker or muscle relaxant used in modern anaesthesia, to facilitate endotracheal intubation and to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. Introduced in 1994, rocuronium has rapid onset, and intermediate duration of action. It is commonly marketed under the trade names Zemuron and Esmeron. The drug is associated with the risk of developing allergic reactions in some high-risk patients, such as those with asthma. However, there was a similar incidence of allergic reactions associated with other non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents. Sugammadex is a γ-cyclodextrin derivative that has been introduced as a novel agent to reverse the action of rocuronium. ****
Ropivacaine is an aminoamide local anesthetic drug marketed by AstraZeneca under the trade name Naropin. It exists as a racemate of its S- and R-enantiomers, although the marketed form is supplied only as the purified S-enantiomer.2 ****
Sodium bicarbonate is a compound used for the symptomatic treatment of heartburn, acid indigestion, and upset stomach as well as the treatment of metabolic acidosis associated with conditions such as severe renal disease and circulatory insufficiency due to shock. ****
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. Sodium chloride is the primary salt in seawater and in the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms. It is listed on the World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines. ****
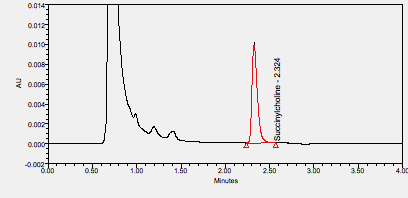
Succinylcholine is a depolarizing skeletal muscle relaxant consisting of two molecules of the endogenous neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) linked by their acetyl groups.2 It has been widely used for over 50 years,1 most commonly in its chloride salt form, as a means of neuromuscular blockade during intubation and surgical procedures. Its rapid onset and offset, with effects beginning within 60 seconds of intravenous administration and lasting between four to six minutes, make succinylcholine particularly useful in the setting of short medical procedures requiring brief periods of muscle relaxation.9 ****
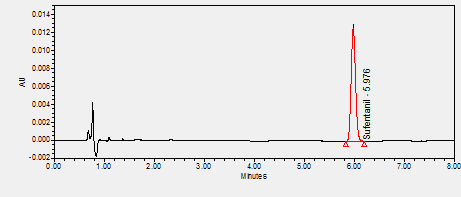
Sufentanil is an opioid used to induce and maintain anesthesia, to act as an analgesic in labor and delivery, and to treat severe, acute pain. ****
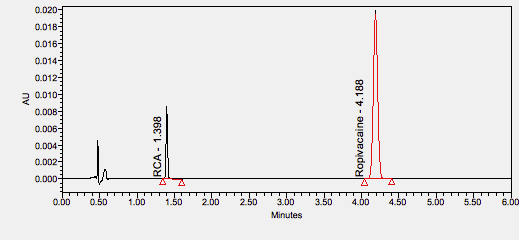
Bupivacaine is a local anesthetic used in a wide variety of superficial and invasive procedures. ****
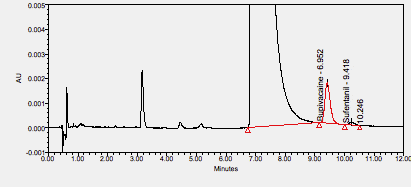
Ropivacaine is an amide-type local anesthetic used for local or regional anesthesia during surgery and for short-term management of acute pain. ****
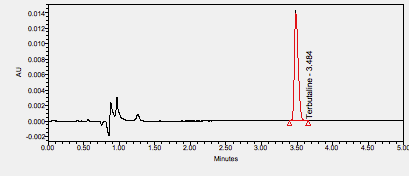
Terbutaline is a beta-2 adrenergic agonist used as a bronchodilator and to prevent premature labor. ****
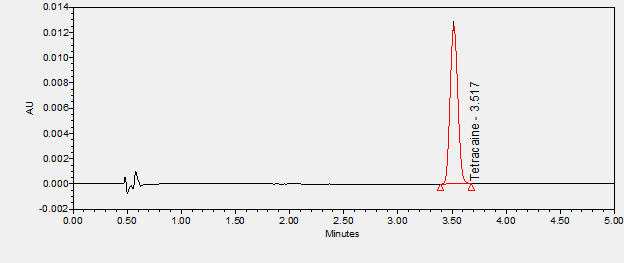
Tetracaine is a local anaesthetic agent used to induce local analgesia in the eyes and skin during medical procedures. ****
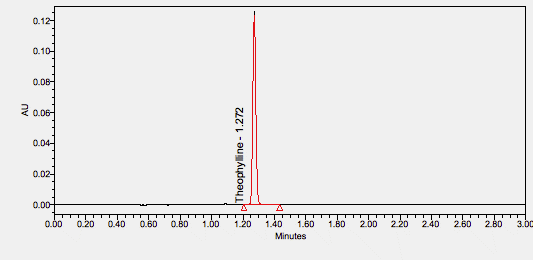
A methylxanthine derivative from tea with diuretic, smooth muscle relaxant, bronchial dilation, cardiac and central nervous system stimulant activities. Mechanistically, theophylline acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, adenosine receptor blocker, and histone deacetylase activator. Theophylline is marketed under several brand names such as Uniphyl and Theochron, and it is indicated mainly for asthma, bronchospasm, and COPD. ****
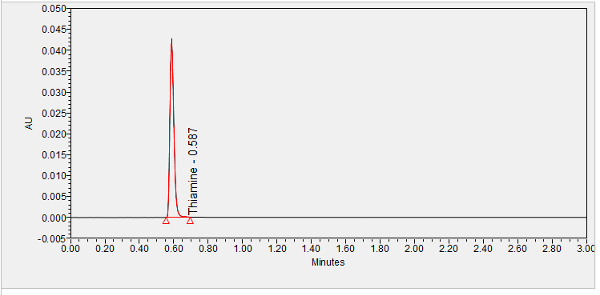
Thiamine or thiamin, also known as vitamin B1, is a colorless compound with the chemical formula C12H17N4OS. It is soluble in water and insoluble in alcohol. Thiamine decomposes if heated. Thiamine was first discovered by Umetaro Suzuki in Japan when researching how rice bran cured patients of Beriberi. Thiamine plays a key role in intracellular glucose metabolism and it is thought that thiamine inhibits the effect of glucose and insulin on arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation. Thiamine plays an important role in helping the body convert carbohydrates and fat into energy. It is essential for normal growth and development and helps to maintain proper functioning of the heart and the nervous and digestive systems. Thiamine cannot be stored in the body; however, once absorbed, the vitamin is concentrated in muscle tissue. ****
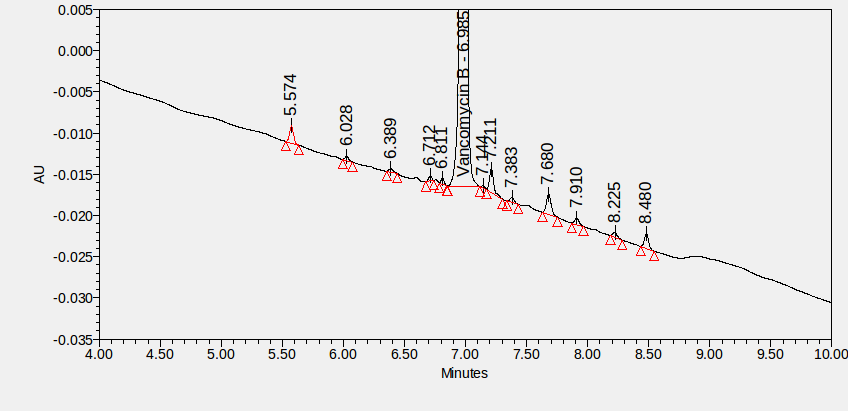
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic used to treat severe but susceptible bacterial infections such as MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) infections. ****
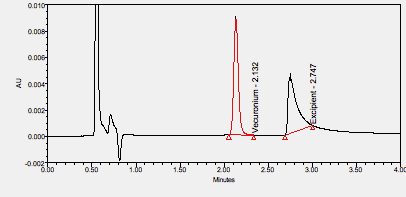
Vecuronium is a nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent used to relax muscles or as an adjunct in general anesthesia during surgical procedures. ****
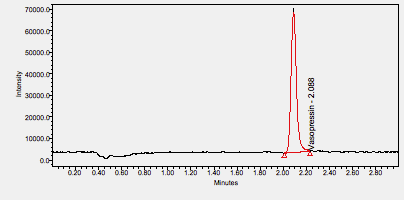
Vasopressin is a peptide hormone used to increase blood pressure in patients with vasodilatory shock who are resistant to fluid and catecholamine therapy. ****
Creating unrivaled capacity for timely results.
Prompt Praxis Laboratories, analytical testing labs, provide a full range of rapid testing and support services focusing on pharmaceutical products and compounded sterile or nonsterile preparations.
Complete the form below, and we will be in touch shortly.

Prompt Praxis Laboratories, LLC, founded in 2011, is a women-owned fully-integrated analytical and microbiological testing lab powered with the current information technology to facilitate rapid drug development.

FDA Establishment Identifier:
3009381492
GDUFA Self-Identified
Illinois DEA:
(Analytical Laboratory, Schedules II-V)
097.001930
Federal DEA:
(Analytical Laboratory, Schedules II-V)
RM0458097
Phone
Locations
50 Lakeview Parkway, Suite 123
Vernon Hills, IL 60061-1590
150 N Fairway Drive, Suites 148-154
Vernon Hills, IL 60061-1860